According to a poll conducted by Ipsos for the Paper and Packaging Board, 72% of consumers believe that packaging design influences their purchasing decisions, while 67% agree that they choose products based on the packaging material. These statistics underscore the importance of packaging — as a major factor that drives sales and impacts the perception of products.

Packaging boxes combine form and function to protect and convey products, promote brands, and make shipping easier. Made from various materials, mainly paper, cardboard, and plastic, packaging boxes influence the retailing, storage, shipping, advertisement, and environmental impact.
In this blog post, we will discuss the packaging box manufacturing process, from design and planning to quality control.
Design and Planning: From Concept to Creation: Designing Your Packaging Box
Understanding Your Needs
The first step towards manufacturing packaging boxes is understanding your packaging needs. With so many options to choose from, it can be difficult to determine the most suitable choice. Hence, it is important to perform a complete market analysis for information on your competitors, market preferences, and consumer behavior before making a decision. This allows the specification of packaging objectives and encourages distinctiveness in the competitive market.

This includes considering the product dimensions and weight specifications to ensure the right packaging size and shape are used. Selecting a preferred box style will determine how protective and functional the package will be. Some styles to choose from include corrugated, folding cartons, and rigid boxes. Also, branding and aesthetic requirements like logo, color, and finishes are important elements to make the packaging attractive to your target audience.
Structural Design
The structural design of packaging boxes is crucial as it influences the durability, functionality, and aesthetic appeal of packages. Using CAD software like Adobe Illustrator, ArtiosCad, and AutoCAD, packaging box mockups are edited and modeled to follow precise dimensions and meet industry standards. These designs are crafted to enhance the visual appeal of packages on store shelves and online platforms.
A key step in the packaging box manufacturing process is the creation of dielines. Dielines are an important blueprint of packaging design, which serve as templates for cutting and folding the packaging material. They aid in establishing the product size and dimensions, visual element placement, and achieving consistency in structural features.
Precise and accurate measurements are vital in packaging design as they enable refined packaging designs and minimal waste while maintaining protection. In addition, high-precision testing ensures adherence to strict packaging regulations, such as ASTM, ISTA, and ISO.
Material Selection
Selecting the right packaging material for boxes is vital to meeting your customer preferences, safeguarding products, and maintaining brand integrity. Some of the most popular cardboard types used for packaging boxes are corrugated cardboard, chipboard, and solid bleached sulfate (SBS). These materials offer different advantages and are used depending on the packaging requirements.

Corrugated cardboard offers robust protection across diverse products. They are durable, stackable, and customizable, guaranteeing item integrity during handling and transit. Made from wood chips, sawmill shavings, and resin, chipboard is used to create lightweight sturdy boxes for various applications. On the other hand, SBS paperboard is highly appreciated for its strength, consistency, and superior printing surface. This packaging material is often preferred for premium packaging and printing applications.
When choosing a material, it’s important to consider the material cost, ensuring it aligns with your packaging budget. Another essential factor is strength and durability. This is to make sure that products are protected during shipping and storage, as well as during the supply chain process.
Additionally, sustainability plays a growing role in the packaging industry as consumers prefer materials that are recyclable or biodegradable. Ultimately, a professional printed box packaging manufacturer will use materials that satisfy all important factors, guaranteeing product protection, cost efficiency, and sustainability.
Printing: Bringing Your Design to Life: The Printing Process
Pre-Press
The pre-press process of printing packaging boxes begins with preparing artwork files using industry-standard software like Adobe Illustrator or ArtiosCAD. When the artwork is well-prepared, it ensures a smooth printing and cardboard box manufacturing process. This is because minimal time is wasted for modification and errors are easily avoided, thereby reducing production costs.
Some good practices implemented by designers during artwork creation include using several layers in the software, working in the correct color mode (CMYK or Pantone), outlining the artwork texts, embedding linked files or images, adding a bleeding area during designing, and using a dieline template.

As soon as the artwork is ready, the next step is creating printing plates or screens. The creation of plates depends on the printing method being used. Flexography printing employs a flexible relief plate made of rubber wrapped around a cylinder, while offset printing makes use of aluminum plates from which images are transferred to a rubber blanket for processing. Alternatively, screen printing uses a woven silkscreen for manual or semi-automated applications.
Printing Methods
Flexography
Flexographic printing is an efficient, versatile, and widely used technique for creating high-quality printed materials. It involves the use of flexible photopolymer printing plates to print high-resolution images on a variety of substrates. These rubber plates are imprinted with a raised image and then wrapped around cylinders mounted on a web press. Having been fed to the press, the substrate moves through and the inked plates transfer the desired image or text onto it. In flexographic printing, each color requires a different plate.

This printing method is widely used for corrugated boxes, labels, and flexible films due to its cost-effectiveness and fast-drying inks. It is ideal for large-scale production, ensuring consistent quality on different substrates like paper, plastic, and cardboard.
Offset Lithography
Offset lithography, also known as offset printing, is a method of printing in which the images on metal plates are transferred (offset) to rubber blankets and then to the printing surface. The flexible rubber blanket readily conforms to the print media surface, allowing for easy printing on rough surfaces such as canvas, cloth, or wood.

This printing technique is ideal for high-volume production, offering high and consistent image quality and color accuracy. Common applications of offset lithography include brochures, magazines, packaging boxes, and business cards. While his method works best on smooth surfaces like paper and cardboard, it is also effective on rough surfaces.
Digital Printing
Digital printing transfers digital files directly onto a variety of media substrates. Unlike offset and flexographic printing, there is no need for a printing plate. Digital files, such as PDFs, can be sent directly to the digital printing press to print on paper canvas, fabric, synthetics, and cardstock, among other substrates.
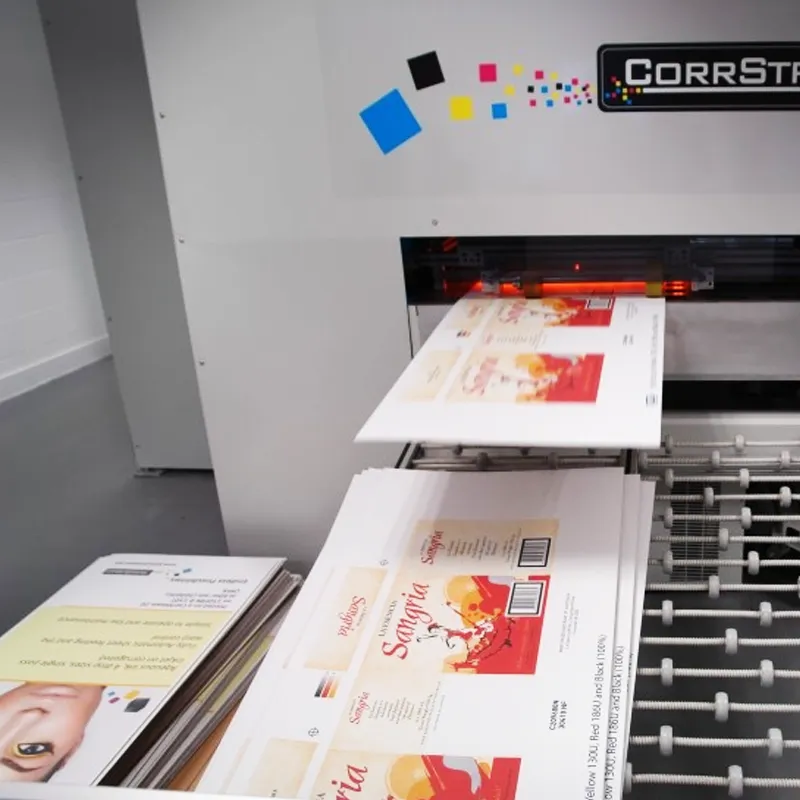

Digital printing is ideal for small, high-quality print runs as well as customizable prints. This technique offers fast turnaround times and low cost per unit for packaging boxes. Some applications of digital printing in packaging and production include marketing materials, labels, and personalized prints.
Post-Press (Optional)
Post-press in the packaging box manufacturing process involves applying “film” laminates or liquid coatings that improve the look and feel of the package. Most coatings and laminates can be combined with other extras, such as embossing or debossing, to make beautiful packaging boxes. Coated packages have a protective water-resistant layer on the surface of paper-based packaging materials. Some popular coating types are varnish, aqueous, and UV coatings, which prevent moisture from penetrating and create a high-gloss finish for a premium look.
Also called foil or film, lamination is a printed layer that covers the entire surface of your box, adding extra strength, durability, and extraordinary finishing. While gloss lamination provides a vibrant, reflective finish, matte lamination gives a soft, sophisticated appearance.
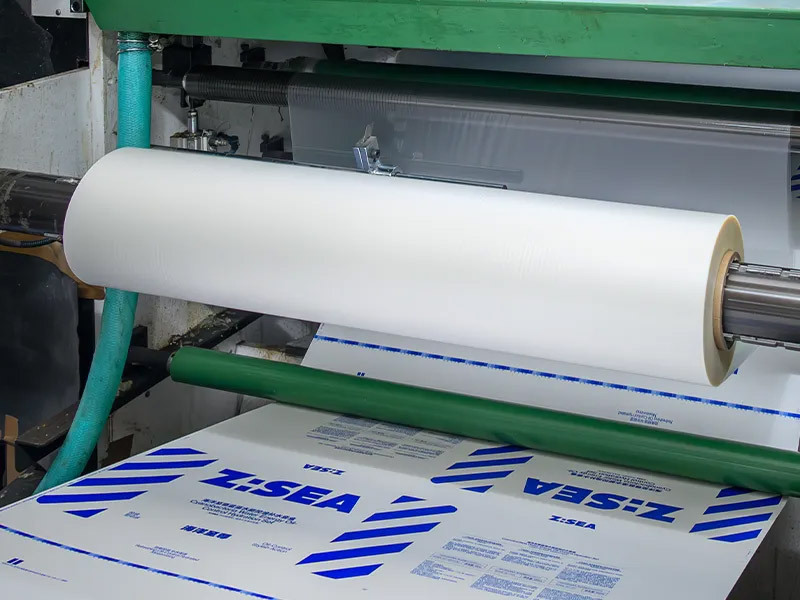

For creating paper packaging samples with a unique and attractive appearance, embossing and debossing are great techniques. Embossing adds depth and texture to help details and patterns emerge from designs, creating a special look on the packages. In contrast, debossing causes details and patterns to sink, causing a strong visual effect.
Die-Cutting: Shaping the Box
Creating the Die
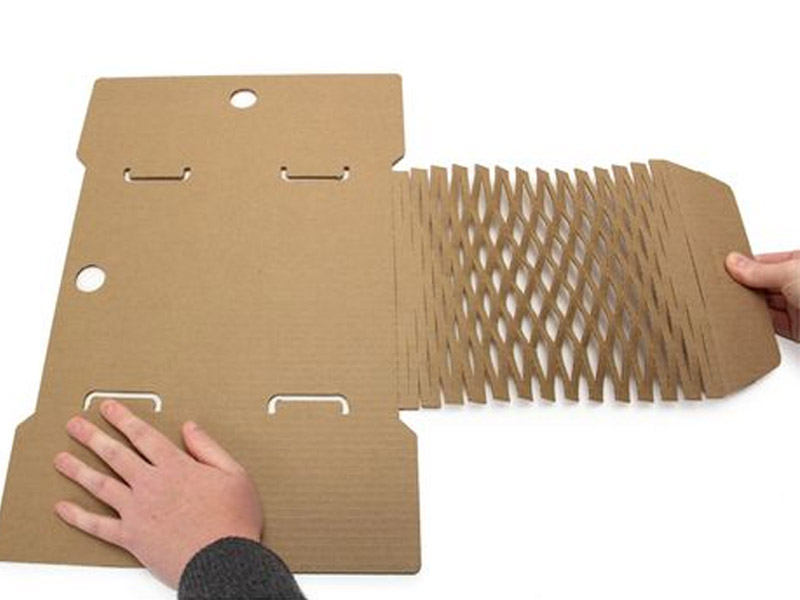
Die-cutting is a carton box manufacturing process that uses a pre-designed template to cut cardboard sheets into boxes of different shapes, designs, and patterns. The die outlines the box’s dimensions, including folding lines, cutouts, and perforations, allowing for seamless assembly.
There is a range of materials used for die-making, including hardened steel, carbon block steel, carbide, plywood, and aluminum. The material used for die-making depends on the production scale and the material being cut. Using the right die ensures efficient production, minimal material waste, and a professional finish.
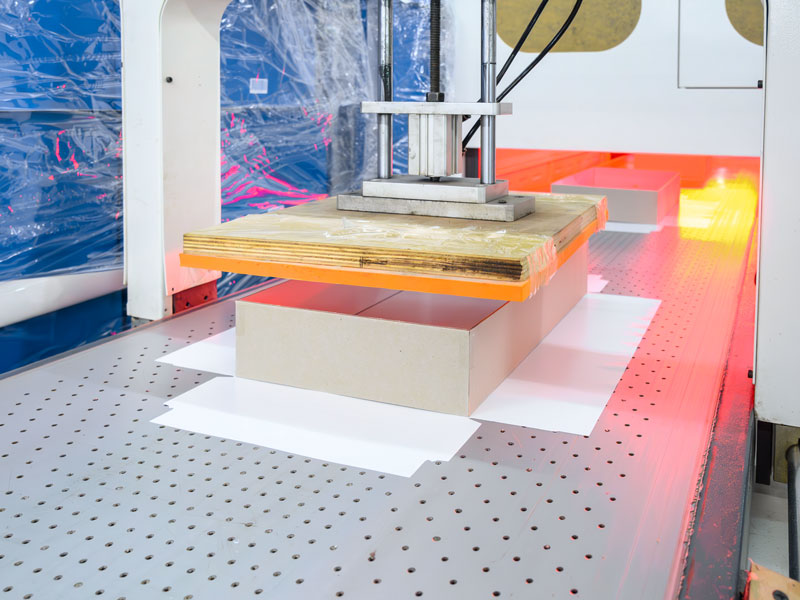
The Die-Cutting Process
Die-cutting machines are used in packaging processes and molded pulp manufacturing to cut materials into precise packaging boxes with exceptional accuracy. They come in various types, each suitable for different applications:
- Manual die cutters: These machines use steel-cutting dies activated by a lever.
- Digital die cutters: Instead of a steel die, digital die cutters use a sharp blade to cut the material. These machines employ software applications and electricity to function.
- Industrial die cutters: For large-scale manufacturing, industrial die cutters are used. These machines automate the cutting process to speed up the production of shapes.
Based on its mode of operation, die cutting is divided into rotary and flatbed. Rotary die cutting involves the use of a cylindrical die on a rotary press to cut the cardboard into the desired shape, while flatbed die cutting uses a flatbed die cutting press and custom steel dies to convert the material into custom shapes.
For high-volume production runs, rotary die cutting is suitable as it is quick and consistent. Comparatively, flatbed cutting is an ideal choice for lower volumes and thicker materials.
Stripping and Waste Removal
After die-cutting, the next step in the packaging box manufacturing process is stripping and waste removal. This involves removing the waste pieces of material (scraps) from the die-cut blanks, ensuring that only the desired shape remains. Stripping enhances the cleanliness and precision of the final product and can be done in two ways: full stripping and partial stripping.
Full stripping removes all the waste of outer and inner holes and is ideal for thick sheets like corrugated boards.
Partial stripping, on the other hand, uses a stripping blade to remove holes and areas that can not be removed by hand. This stripping technique is suitable for thin sheets like cardboard, which are hard to run with limited nick volumes.
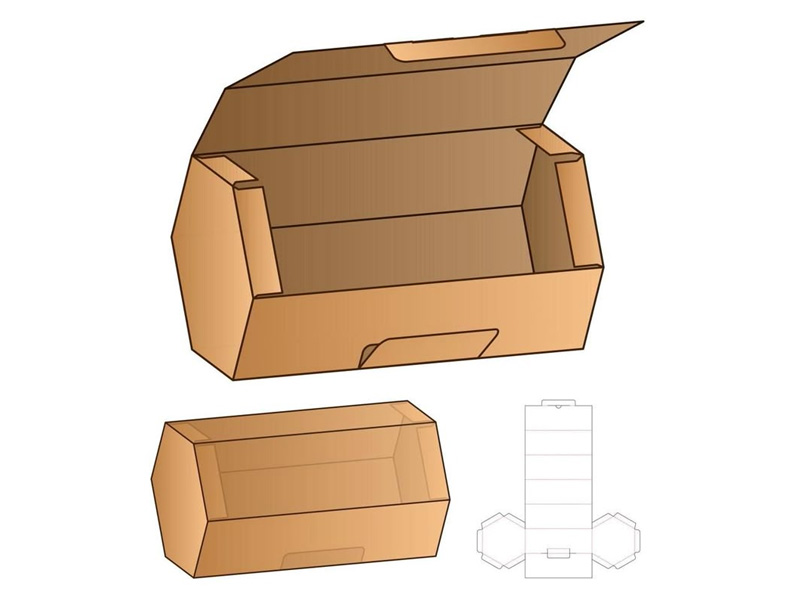
Folding and Gluing: Assembling the Box
Folding
In the final stages of packaging manufacturing, flat, die-cut pieces of material are folded to ensure structural integrity and ease of use. The folding method (automated or manual) used will depend on the requirements of the box and order volume.
Automated folding involves using machines that are made of electronic components to compress and fold paper or cardboard into a box. They are preferred for large-scale production. These machines handle high-volume orders with speed and accuracy, making them ideal for mass production of packaging boxes.
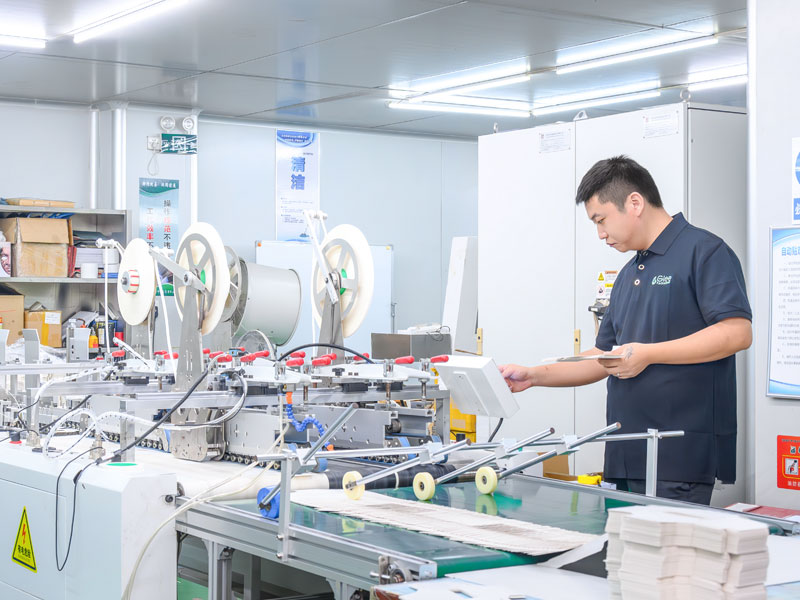

Manual folding is more suitable for smaller-volume runs or complex designs. This method allows for greater flexibility in handling custom packaging that may not be compatible with automated processes. During this process, skilled workers fold and assemble boxes by hand, ensuring attention to detail and quality control.
Gluing
Gluing refers to the technique used to assemble and secure different parts of the packaging. This is essential to make your packaging boxes not only look good but also hold together under stress and protect their contents effectively. Depending on the packaging material, there are various types of glues used to ensure secure assembly. Some of these include hot-melt adhesives, starch-based adhesives, water-based adhesives, and solvent-based adhesives.
In addition, different gluing methods can be used to create sturdy box structures. One of the popular methods of gluing is side seam gluing, which involves joining the box edges to create strong packages. Alternatively, bottom gluing reinforces the packaging base, allowing for a reliable assembly.
Manual gluing remains a viable option for small-scale, unique, or custom packaging, as operators apply glue using brushes, rollers, or glue guns. Whereas, automated gluing machines enhance efficiency in large-scale production.
Quality Control
After the package assembly, the next vital step is quality control. This step ensures that all packages meet the required standards and specifications before they leave the factory floor. Quality control is crucial for sustaining brand reputation and improving consumer loyalty, as well as reducing waste and return rates.
Key aspects of quality control in packaging and production include visual inspection, physical testing, and compliance verification.
Eco-Friendly Packaging: Sustainable Practices
Eco-friendly packaging refers to packaging materials and practices that are environmentally sustainable and have the lowest possible impact on the environment. These materials can be obtained from renewable resources or recycled materials that are designed to be biodegradable or compostable.
The importance of sustainability can not be overstated as being green is important to consumers now more than ever. According to a study done by Shopify, sustainable practices help customers maintain stronger relationships with brands, resulting in a 306% higher lifetime value.
Hence, implementing eco-friendly practices is essential for the growth of your brand and the longevity of your business. Moreover, traditional packaging has had a negative global impact on the environment and recyclable packages are safer for the world.
One of the most effective ways to achieve eco-friendly packaging is by sustainable sourcing of raw materials. This involves using FSC-certified paper, responsibly harvested wood pulp, and plant-based alternatives, ensuring that packaging production does not contribute to deforestation or habitat destruction.
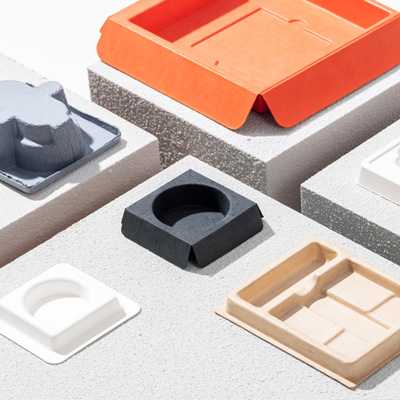

The use of lightweight packaging, minimalistic design, and other eco-friendly processes help to reduce the amount of waste in landfills and lower carbon emissions. This mitigates climate change impact and decreases the environmental footprint associated with traditional packaging.
Biodegradable and compostable packaging options, such as cornstarch-based bioplastics, mushroom packaging, and kraft paper, provide sustainable alternatives that decompose naturally without harming the environment. By integrating recycled content, sustainable sourcing, waste reduction, and compostable materials, you can create packaging solutions that are both functional and environmentally responsible, contributing to a greener future.
Conclusion
The packaging box manufacturing process is essential for brands looking to create functional and visually appealing packages. Each step, from designing and planning to quality control, plays a meaningful role in ensuring the packaging boxes stand out on the shelves and satisfy customers’ needs. By focusing on each stage of the process, you can deliver packaging that secures and preserves products, as well as improve your brand image and market presence.


